The Bar Magnet
The Bar Magnet: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Magnetism, Bar Magnet, Magnetic Field Lines of a Bar Magnet, Bar Magnet as an Equivalent Solenoid, Pole Strength, Bar Magnet as Magnetic Dipole, Magnetic Dipole Moment of a Bar Magnet, Magnetic Monopole, etc.
Important Questions on The Bar Magnet
A bar magnet of magnetic moment is bent to form a semicircle. What is the magnetic moment of the bent magnet?
The magnetic field lines due to a bar magnet are correctly shown in
Two magnetic are as shown in figure. Force between them is
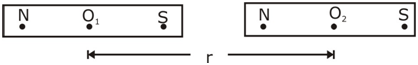
The short bar magnetic are placed as shown in figure. The magnetic of force between them is proportional to
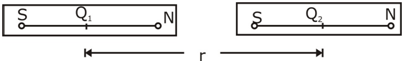
If two short bar magnetic are placing the line joining then as shown in the figure. Nature of force between two magnetic is
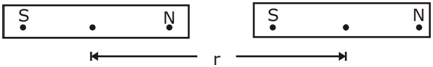
Is it possible to isolate the poles of a magnet?
Two lines of force due to a bar magnet:
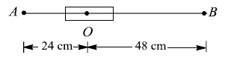
A bar magnet of length has a point and along axis at a distance of and on the opposite ends. Ratio of magnetic fields at these points will be
The effect on a freely suspended magnetic needle due to a uniform magnetic field is as follow.
The magnetic moment of a bar magnet is . Its pole strength is . Its magnetic length is
A magnet makes oscillations per minute at a place having earth's horizontal magnetic field intensity of . At another place, it takes to complete one vibration. The value of earth's horizontal field at that place is
The areas of cross-sections of three magnets of same length are and respectively. The ratio of their magnetic moments will be
A magnetic dipole is acted upon by two magnetic fields which are inclined to each other at an angle of . One of the fields has a magnitude of . The dipole attains stable equilibrium at an angle of with this field. The magnitude of the other field (in mT) is close to:
A circular loop with turns has radius . It lies in the x-y plane carrying current in the anti-clockwise direction. If the magnetic field in the region is then find the torque acting on the loop.
Assertion: Poles of a magnet can never be separated.
Reason: Since each atom of a magnetic material is a magnet in itself.
A bar magnet of length has a point and along axis at a distance of and on the opposite ends. Ratio of magnetic fields at these points will be
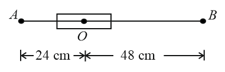
Two short bar magnets with magnetic moments and are placed with their axis in the same straight line with similar poles facing each other and with their centers at from each other. Then the force of repulsion is
The areas of cross-section of three magnets of same length area and respectively. The ratio of their magnetic moments will be
Potential energy of a bar magnet of magnetic moment placed in a magnetic field of induction such that it makes an angle with the direction of is
